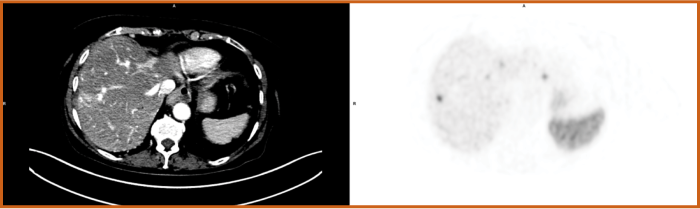
Clear, high-accuracy imaging with Detectnet can help you obtain a precise patient picture and determine the right treatment plan1,2

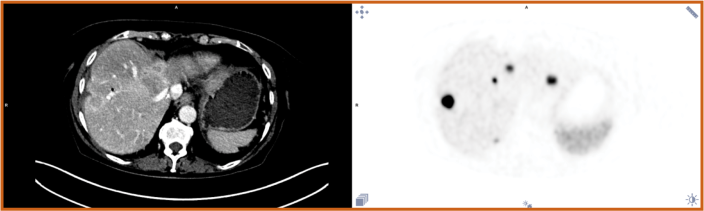
Detectnet's clear, sensitive imaging enables you to confidently differentiate between local and metastatic lesions2


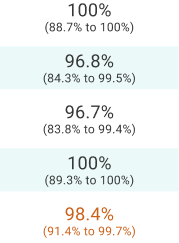
Study 1: Delpassand 2020 demonstrated sensitivity and specificity of 100% to differentiate between localized and metastatic disease.2
Study 1: Delpassand 2020 study design2
A phase 3, open-label, single-dose, single-arm, single-center prospective study to evaluate the diagnostic performance and safety of Detectnet PET/computed tomography (CT) imaging in 63 participants (42 patients with known or suspected NETs and 21 healthy volunteers). Detectnet results, read by blinded experts, were compared with a reference standard based on an independent expert’s assessment of conventional imaging and clinical and laboratory data. PET/CT scans were taken ~60 minutes after a single IV dose of 148 MBq ± 10% of Detectnet.
Considerations: The reference standard incorrectly identified 3 NET-negative cases as NET-positive. Because the objective of the study was to assess the performance of the PET/CT scan and not the reference standard, the corrected values are shown.
This trial was not designed as a superiority study. Clinical follow-up was at least 30 months.
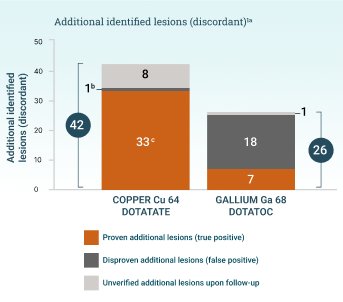
aThe patient-level diagnostic performance was the same for both tracers because they were both able to identify matching lesions in patients where additional lesions were also identified. 701 matching (concordant) lesions were identified.
bReported significant, but no P value included.
cP<.001.
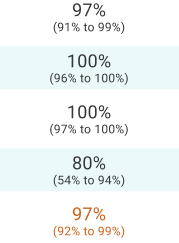
A head-to-head study with gallium Ga 68 dotatoc (Johnbeck 2017) demonstrated copper Cu 64 dotatate's high lesion detection rate.1 The authors concluded that “the difference in lesion detection rate found in the current study is presumed to relate to use of 64Cu instead of 68Ga rather than to differences in peptide.”1
Johnbeck 2017 study design
A prospective, open-label, single-center, European head-to-head study to assess the diagnostic performance of copper Cu 64 dotatate PET/CT and gallium Ga 68 dotatoc PET/CT in 59 patients with NETs. PET scans were acquired 1 hour after injection of ~200 MBq of copper Cu 64 dotatate or 45 minutes after injection of 150 MBq of gallium Ga 68 dotatoc. Imaging with copper Cu 64 dotatate and gallium Ga 68 dotatoc was conducted within 1 week of each other. Clinical follow-up was at least 30 months.1
Considerations: The recommended dose of Detectnet is 148 MBq.3 A diagnostic CT scan was acquired only with copper Cu 64 dotatate PET, which could impact the ability to detect small lesions; however, lesion-to-lesion comparison of the images mitigated this concern. This study was not designed to assess superiority.1


Get Connected
INDICATION and IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION


IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Radiation Risk:
Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals, including Detectnet, contribute to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Ensure safe handling and preparation procedures to protect patients and health care workers from unintentional radiation exposure. Advise patients to hydrate before and after administration and to void frequently after administration.
Hypersensitivity Reactions:
Hypersensitivity reactions following administration of somatostatin receptor imaging agents predominantly consisted of cutaneous reactions such as rash and pruritus. Reactions reversed either spontaneously or with routine symptomatic management. Less frequently hypersensitivity reactions included angioedema or cases with features of anaphylaxis.
Risk for Image Misinterpretation:
The uptake of copper Cu 64 dotatate reflects the level of somatostatin receptor density in NETs, however, uptake can also be seen in a variety of other tumors that also express somatostatin receptors. Increased uptake might also be seen in other non-cancerous pathologic conditions that express somatostatin receptors including thyroid disease or in subacute inflammation, or might occur as a normal physiologic variant (e.g., uncinate process of the pancreas).
A negative scan after the administration of Detectnet in patients who do not have a history of NET disease does not rule out disease.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical trials, adverse reactions occurred at a rate of < 2% and included nausea, vomiting and flushing. In published trials nausea immediately after injection was observed.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Somatostatin Analogs:
Non-radioactive somatostatin analogs and copper Cu 64 dotatate competitively bind to somatostatin receptors (SSTR2). Image patients just prior to dosing with somatostatin analogs. For patients on long-acting somatostatin analogs, a washout period of 28 days is recommended prior to imaging. For patients on short-acting somatostatin analogs, a washout period of 2 days is recommended prior to imaging.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy:
All radiopharmaceuticals, including Detectnet have the potential to cause fetal harm depending on the fetal stage of development and the magnitude of the radiation dose. Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risks of fetal exposure to radiation from administration of Detectnet.
Lactation:
Advise a lactating woman to interrupt breastfeeding for 12 hours after Detectnet administration in order to minimize radiation exposure to a breastfed infant.
Pediatric Use:
The safety and effectiveness of Detectnet have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use:
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of a radiation overdose, the absorbed dose to the patient should be reduced where possible by increasing the elimination of the radionuclide from the body by reinforced hydration and frequent bladder voiding. A diuretic might also be considered.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Detectnet is indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adult patients.
Back to top
References
- Johnbeck CB, Knigge U, Loft A, et al. Head-to-head comparison of 64Cu-DOTATATE and 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT: a prospective study of 59 patients with neuroendocrine tumors. J Nucl Med. 2017;58(3):451-457. doi:10.2967/jnumed.116.180430
- Delpassand ES, Ranganathan D, Wagh N, et al. 64Cu-DOTATATE PET/CT for imaging patients with known or suspected somatostatin receptor–positive neuroendocrine tumors: results of the first U.S. prospective, reader-masked clinical trial. J Nucl Med. 2020;61(6):890-896. doi:10.2967/jnumed.119.236091
- Detectnet. Prescribing information. Curium US LLC; January 2025.
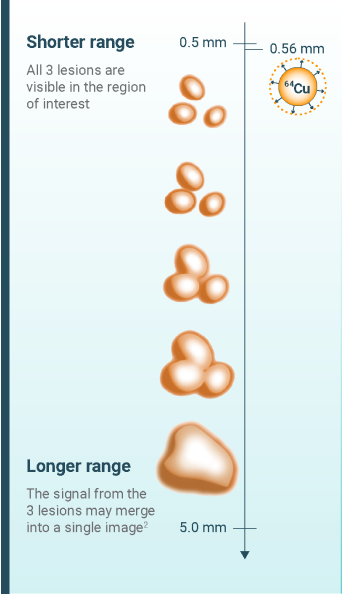
- Conti M, Eriksson L. Physics of pure and non-pure positron emitters for PET: a review and a discussion. EJNMMI Phys. 2016;3(1):8. doi:10.1186/s40658-016-0144-5
- Alva-Sánchez H, Quintana-Bautista C, Martínez-Dávalos A, Ávila-Rodríguez MA, Rodríguez-Villafuerte M. Positron range in tissue-equivalent materials: experimental microPET studies. Phys Med Biol. 2016;61(17):6307-6321. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/61/17/6307
- Schäfers KP. The promise of nuclear medicine technology: status and future perspective of high-resolution whole-body PET. Phys Med. 2008;24(2):57-62. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2008.01.008
- Singh S, Granberg D, Wolin E, et al. Patient-reported burden of a neuroendocrine tumor (NET) diagnosis: results from the first global survey of patients with NETs. J Glob Oncol. 2016;3(1):43-53. doi:10.1200/JGO.2015.002980
- Pfeifer A, Knigge U, Binderup T, et al. 64Cu-DOTATATE PET for neuroendocrine tumors: a prospective head-to-head comparison with 111In-DTPA-octreotide in 112 patients. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(6):847-854. doi:10.2967/jnumed.115.156539
- Hope TA. Updates to the appropriate-use criteria for somatostatin receptor PET. J Nucl Med. 2020;61(12):1764. doi:10.2967/jnumed.120.257808
- Lutathera. Prescribing information. Novartis AG; October 2024
- Data on file. Curium US LLC.